 Problem statement
Problem statement
In the context of increasingly scarce energy resources and continuously rising electricity costs, energy saving in factories has become not only an urgent requirement but also an inevitable trend of the industrial sector in Vietnam. Along with the pressure from global environmental standards and market demands for environmentally friendly products, businesses must find ways to optimize energy efficiency to reduce operating costs, increase competitiveness and meet the needs of sustainable development. Investing in energy saving solutions not only helps factories cut costs but also contributes to the goal of sustainable development, while meeting strict regulations on emissions and environmental protection. Therefore, energy saving has become a common development trend of factories and industries in Vietnam in the current period.
LOTUS NC Certification for Energy Saving in Factories
LOTUS NC is the first voluntary green building rating system for new construction developed specifically for the construction market in Vietnam, created by the Vietnam Green Building Council (VGBC). In Vietnam, VGBC has established the Vietnam Green Building Social Enterprise Company Limited to carry out LOTUS project assessment and certification activities and related training programs.
Developed based on established building physics science and suitable for conditions, climates as well as complying with Vietnamese Standards and Regulations, LOTUS NC provides a comprehensive assessment of the environmental performance of buildings and structures. The system provides an integrated approach to assessing buildings including energy consumption, water use and waste management as well as indoor environmental quality. It serves as an objective assessment system that can be used by any stakeholder in the construction process – developers, designers, contractors and owners – for a variety of purposes.
As of 2024, a total of 12 factories in Vietnam have achieved LOTUS certification, of which 11 have been officially recognized. The calculation of energy saving in these factories is carried out through simulations based on the baseline model prescribed by VGBC and the actual design model of each project. This article provides detailed data related to energy efficiency in factory design and construction according to the criteria of LOTUS NC version V2 and V3.
Figure 1. Percentage of E-2 Credit Energy Savings of New Building Projects with LOTUS NC Certification
From the graph in Figure 1, we see that the highest energy savings of some factories reached 62%, while the lowest was 20%, and both belonged to projects aiming for LOTUS NC V2 certification. In contrast, factory projects aiming for LOTUS NC V3 certification showed lower energy savings, with a maximum of 48% and a minimum of 21%.
When calculating the average, factory projects following LOTUS NC V2 achieved an average energy savings of 39% (equivalent to 11 points), while projects following LOTUS NC V3 achieved an average savings of 35% (equivalent to 10 points). Overall, the average energy savings for all factory projects that achieved LOTUS certification was 38%.
In particular, when considering credit points, 3 projects, accounting for 27.3% of the total number of projects, exceeded the maximum score. This shows that with an energy saving level of 35% (10 points) according to LOTUS NC V3, the possibility of achieving a maximum saving level of 45% (14 points) for factory projects is completely feasible through the application of renewable energy solutions such as rooftop solar power systems. This is not only a sustainable energy trend for green buildings but also an important development orientation for green factories in the future.
LOTUS NC Certification for Water Saving Targets in Factories
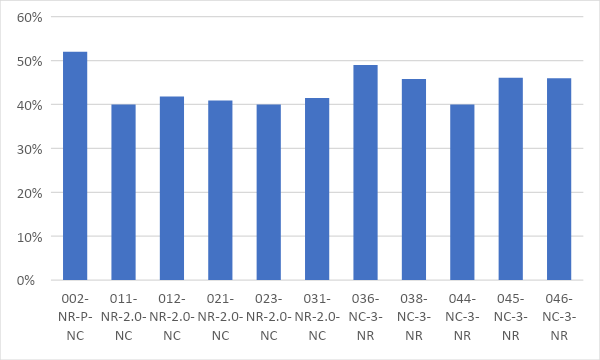
Figure 2. Indoor water savings chart by W-1 credits of factory projects that have obtained LOTUS NC certification
Figure 2 illustrates the water savings chart of the plants, showing that some projects achieved impressive water savings, with the highest being 50%, while the lowest was 40%. These benchmarks were set for projects applying the LOTUS NC V2 standard. For plant projects applying the LOTUS NC V3 standard, water savings also reached 49% at the maximum level and 40% at the minimum level, similar to the values achieved in the LOTUS NC V2 version.
On average, projects applying the LOTUS NC V2 achieved a water savings of 43% (equivalent to 5 points), exceeding the maximum requirement of 40%. Meanwhile, projects following the current version of LOTUS NC V3 maintained a water savings of 45% (equivalent to 5 points), which is also the maximum requirement. An average water savings of 44% was recorded for all LOTUS certified factory projects.
With an average water savings of 44% for both LOTUS NC V2 and V3, the potential for a maximum savings of 45% (5 points) is very feasible. This is especially true in the context of projects that have the ability to utilize a large enough surface area to store rain water, especially in areas with high rainfall monsoon climates like Vietnam. This is not only a popular water saving trend for green buildings but also an important development direction for green factories, aiming at the goal of net water consumption balance.
The conclusion from the above statistical data shows that most factories achieved significant scores on the energy and water saving criteria according to LOTUS NC. These are important criteria, bringing great sustainable benefits to the projects and the entire industry. Therefore, green factories are becoming a key driver to achieve the net zero emissions target in the green construction sector in Vietnam.
Conclusion
Energy saving in factories is not only a series of integrated technical solutions but also a compilation of sustainable development strategies, playing a key role in building a green economy and industry in Vietnam. The application of energy saving measures not only helps businesses reduce operating costs and improve production efficiency, but also contributes to environmental protection, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and complies with international standards on sustainable development. In the context of global economic integration and facing the challenges of climate change, moving towards green development through energy saving in factories is not only an inevitable trend but also a social responsibility of each business, contributing to creating a sustainable and prosperous industry for Vietnam.
Douglas Snyder, Tran Minh Ngoc, Nguyen Hoang Nhan, Nguyen Dang Nghia
 Problem statement
Problem statement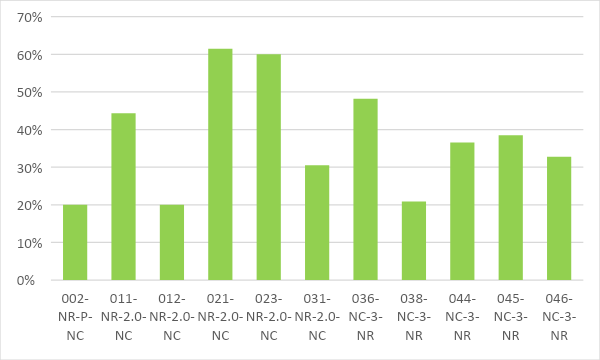

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt





